Table Of Content
The observers then categorize participants individually in terms of which behavior they have engaged in and the number of times they engaged in each behavior. The target behaviors must be defined in such a way that different observers code them in the same way. Researchers are expected to demonstrate the inter-rater reliability of their coding procedure by having multiple raters code the same behaviors independently and then showing that the different observers are in close agreement. The two observers showed that they agreed on the reactions that were exhibited 97% of the time, indicating good inter-rater reliability. A statistic that measures the strength of a correlation between quantitative variables. Another approach to correlational research is the use of archival data, which are data that have already been collected for some other purpose.
To Investigate Variables Without Manipulating Them
Researchers collect data by asking participants to complete questionnaires or surveys that measure different variables of interest. Surveys are useful for exploring the relationships between variables such as personality traits, attitudes, and behaviors. The following section on multiple regression analysis (MRA) describes simultaneous and sequential MRA, the types of information provided by MRA, the problem of multicollinearity, and MRA as an alternative to analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Psychology Research Methods
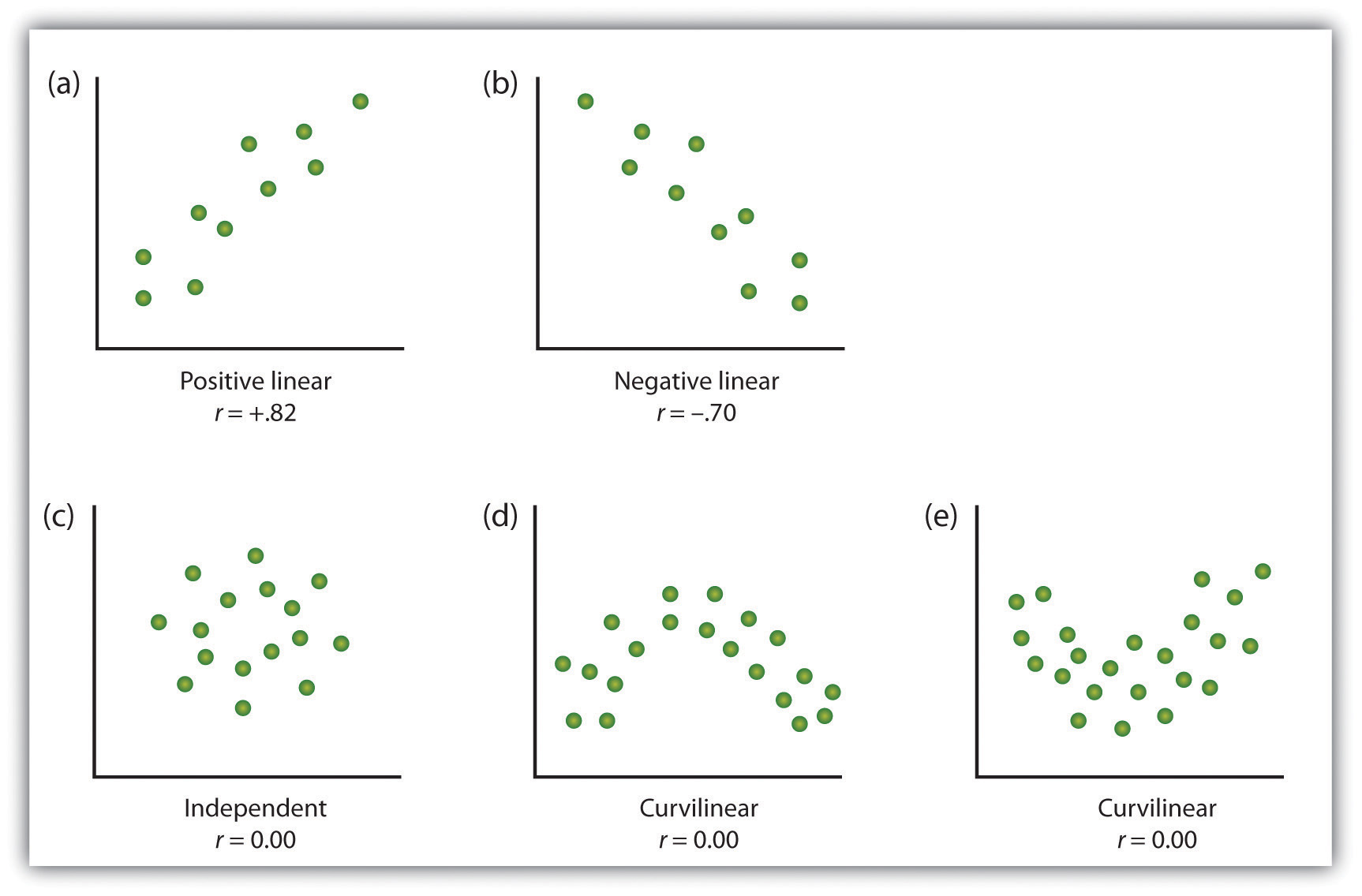
The correlation coefficient (r) indicates the extent to which the pairs of numbers for these two variables lie on a straight line. Values over zero indicate a positive correlation, while values under zero indicate a negative correlation. Cross-sectional studies can help identify potential risk factors for certain conditions or illnesses, and can also be used to evaluate the prevalence of certain behaviors, attitudes, or beliefs within a population. A negative correlation indicates that as the value of one variable increases, the value of the other variable decreases, while a positive correlation indicates that as the value of one variable increases, the value of the other variable also increases.
New psychology research: Privilege has a smaller influence on positive world beliefs than you think - PsyPost
New psychology research: Privilege has a smaller influence on positive world beliefs than you think.
Posted: Thu, 12 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Correlational Research vs. Experimental Research
The problem where two variables, X and Y, are statistically related either because X causes Y, or because Y causes X, and thus the causal direction of the effect cannot be known. Some of the main problems that can occur in correlational research include selection bias, confounding variables. The researchers then compare the exposure history of the cases and controls to determine whether the exposure and health outcome correlate.
For instance, individuals with strong and satisfactory relationships report the highest levels of happiness1,2, and people who have someone to count on in times of need report higher life evaluations worldwide3. Factor analysis is a statistical method used to identify patterns among variables. Researchers use factor analysis to group variables into factors that are related to each other.

We wondered whether the low and relatively stable levels of reaching out in Study 3 may have been a result of the study design, therefore we made two changes in Study 4. First, we took a bottom-up approach to designing the intervention, targeting the particular barriers that participants endorsed in Studies 1–2 when thinking about reaching out to old friends. Additionally, it is possible that we did not detect differences across conditions in Study 3 because the control condition elevated reaching out rates by providing participants with time to write a message. Are people reluctant to reach out to old friends, why might this be, and how can they be encouraged to reconnect? In Study 1, we ask what proportion of people have lost touch with an old friend, how willing they are to reach out, what barriers restrain them, and what reasons would encourage them to reach out.
The goal of correlational research is to examine the relationship between two or more variables. It involves analyzing data to determine if there is a statistically significant connection between the variables being studied. Researchers should use correlational research when they want to investigate the relationship between two variables without manipulating them. This type of research is useful when the researcher cannot or should not manipulate one of the variables or when it is impossible to conduct an experiment due to ethical or practical concerns. There are a number of situations where researchers might opt to use a correlational study instead of some other research design.
Naturalistic Observation
First, the seven studies presented here considered reaching out to an old friend that participants wanted to reconnect with. Not all estranged friendships lapse from neglect; some friendships end on painful or angry terms, offering clear reason for disengagement. We focused on the former context both because we suspected this situation to be common, and because we thought it would provide a generous assessment of reaching out intentions and behaviour. Future researchers could consider how to encourage reaching out, if desirable, in more complicated relational contexts, such as when one or both parties are not eager. Reconnecting with old friends may bring opportunities for social connection and greater well-being, but this only happens if at least one party is willing to reach out.
For example, researchers Robert Kraut and Robert Johnston wanted to study bowlers’ reactions to their shots, both when they were facing the pins and then when they turned toward their companions (Kraut & Johnston, 1979). The observers committed this list to memory and then practiced by coding the reactions of bowlers who had been videotaped. Precise specification of the sampling process in this way makes data collection manageable for the observers, and it also provides some control over important extraneous variables. For example, by making their observations on clear summer days in all countries, Levine and Norenzayan controlled for effects of the weather on people’s walking speeds.
Each cluster is then interpreted as multiple measures of the same underlying construct. The Big Five personality factors have been identified through factor analyses of people’s scores on a large number of more specific traits. For example, measures of warmth, gregariousness, activity level, and positive emotions tend to be highly correlated with each other and are interpreted as representing the construct of extroversion.
These occurrences can then be counted, timed (e.g., the amount of time devoted to entertainment topics on the nightly news show), or analyzed in a variety of other ways. A study is considered correlational if it examines the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them. In other words, the study does not involve the manipulation of an independent variable to see how it affects a dependent variable. An experiment isolates and manipulates the independent variable to observe its effect on the dependent variable and controls the environment in order that extraneous variables may be eliminated. This is an example of content analysis—a family of systematic approaches to measurement using complex archival data. Just as naturalistic observation requires specifying the behaviors of interest and then noting them as they occur, content analysis requires specifying keywords, phrases, or ideas and then finding all occurrences of them in the data.
A correlation reflects the strength and/or direction of the association between two or more variables. But you can’t be certain about whether having low vitamin D levels causes depression, or whether having depression causes reduced intakes of vitamin D through lifestyle or appetite changes. Therefore, you can only conclude that there is a relationship between these two variables. Just because you find a correlation between two things doesn’t mean you can conclude one of them causes the other, for a few reasons.
The chapter concludes with brief discussions of two other forms of correlational analysis, logistic regression analysis and multiway frequency analysis. Finally, a correlational study may include statistical analyses such as correlation coefficients or regression analyses to examine the strength and direction of the relationship between variables. The purpose of correlational research is to examine the relationship between two or more variables.
Factor analysis does not tell us that people are either extroverted or conscientious or that they like either “reflective and complex” music or “intense and rebellious” music. For example, one reason that extroversion and the other Big Five operate as separate factors is that they appear to be controlled by different genes (Plomin, DeFries, McClean, & McGuffin, 2008). As you have learned by reading this book, there are various ways that researchers address the directionality and third-variable problems.
Correlational research can provide initial indications or additional support for theories about causal relationships. When reviewing old research, little information might be available about who conducted the research, how a study was designed, who participated in the research, as well as how data was collected and interpreted. A person might answer a particular way to try to please the researchers or to try to control how the researchers perceive them (such as trying to make themselves "look better"). If researchers need to gather a large amount of data in a short period of time, a survey is likely to be the fastest, easiest, and cheapest option. However, this does not mean that researchers will get reliable data from watching the variables, or that the information they gather will be free from bias. For one, it does not allow them to control or influence the variables in any way nor can they change any possible external variables.

No comments:
Post a Comment